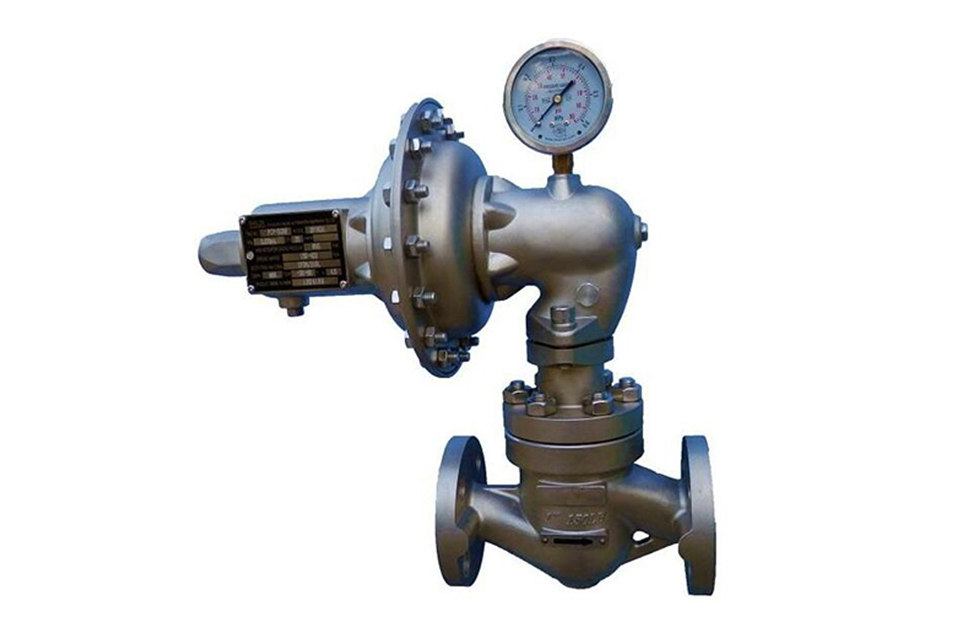
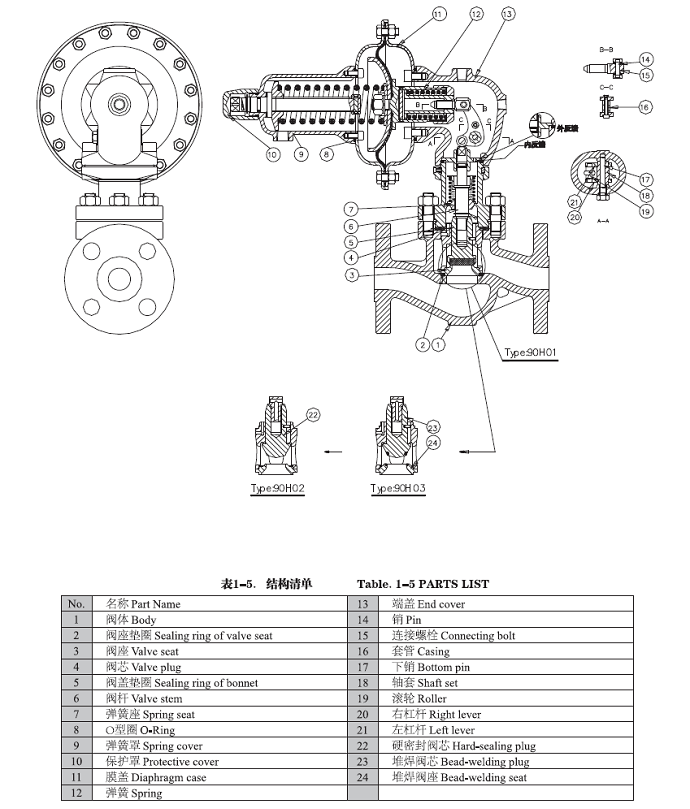
Performance Characteristics
- 1. Compact structure - The built-in spring structure makes the pressure regulating valve more compact and has better protection.
- 2. No packing - Any frictional resistance during micro pressure control will affect the adjustment accuracy of the pressure regulating valve. The no packing structure of this valve provides good sensitivity to the entire pressure regulating structure while reducing external leakage points.
- 3. Thrust amplification - The lever force amplification adjustment mechanism of the pressure regulating valve amplifies the small thrust generated by the diaphragm component by three times, making it have excellent regulation and pressure resistance performance. At the same time, when the downstream system flow rate decreases to "0", the valve core can shut off the fluid in a low-pressure state, keeping the system pressurized.
- 4. Safety overload - Safety is always the most important in any situation. Self regulating valves, due to their medium directly entering the actuator, often cause serious damage to the valve when the system is overpressure. The overload protection mechanism of this valve can safely withstand overload pressures several times or even tens of times higher than the upper limit of the pressure regulation range, and in some configurations, it can fully reach the nominal pressure.
- 5. Easy installation - When the valve leaves the factory, it is impossible to estimate the on-site pipeline direction and installation space. After installation, it is often found that the adjustment of the pressure regulating valve is inconvenient due to the influence of surrounding equipment. The actuator and regulating mechanism of this valve can rotate 360 degrees without disassembly, and the adjustment does not affect its original performance parameters.
Specification Model
| Valve caliber | 1/2"(DN15)~2"(DN50) |
| Nominal pressure | ANSI Class 150#~600# |
| Operating temperature | -48~+120℃ |
| Connection method | Flange type (RF) |
| Valve body material | WCB,CF8,CF8M,CF3,CF3M,etc. |
| Valve core material | 304(L),316(L),etc. |
| Leakage class | ANSI Class IV (Rated Cv × 0.01%) |
| Adjustable ratio | 20:1 |
| Flow characteristic | Standard Normal |
(1) Before installation, check that the product model, tag number, and specifications match the requirements. Inspect the entire valve for missing or loose parts.
(2) Prior to installation, clean the pipeline. Ensure there is sufficient straight pipe section at the valve inlet and install a filter. When connecting the valve body to the pipeline flanges, ensure coaxiality.
(3) Thoroughly clean the pipeline before installing the valve.
(4) The installation site should ensure the safety of personnel and equipment, facilitating operation, disassembly, and maintenance.
(5) The valve should be installed vertically upright on horizontal pipelines. If necessary, it can be installed at an angle, but horizontal installation should be avoided. For occasions with heavy valve weight or vibration, use a support frame.
(6) The medium flow direction must align with the arrow on the valve body. The air supply should be dry and oil-free. The valve should be used in environments with temperatures ranging from -20℃ to 55℃.
(1) Cleaning the Valve: For general media, cleaning with water is sufficient. For media harmful to health, first understand their properties and then select an appropriate cleaning method.
(2) Disassembly: Remove rust from exposed rusted parts first. Before derusting, protect the machined surfaces of precision parts such as the valve seat, valve plug, valve stem, and push rod. Use special tools when disassembling the valve seat.
(3) Valve Seat: Minor rust or wear on the sealing surface can be repaired by machining. If damage is severe, replace the seat. However, both repaired and replaced hard sealing surfaces must be lapped.
(4) Valve Stem: If the surface is damaged, it must be replaced.
(5) Damage to Push Rod, Guide, and Sealing Surfaces: Reverse-acting actuators must be replaced; direct-acting actuators can be reused after proper repair.
(6) Compression Spring: If there are cracks or other defects affecting strength, replace it immediately.
(7) Wear Parts: Packing, gaskets, and O-rings must be replaced entirely during each maintenance. Check the valve plug and diaphragm for cracks, aging, or corrosion that may cause future failures. Decide whether to replace them based on inspection results, but the diaphragm service life should not exceed 2-3 years.
(8) When reassembling the valve, ensure alignment. Tighten bolts diagonally and lubricate sliding parts. After reassembly, debug the valve according to the factory test items and methods. During this period, accurately adjust the packing compression force and the valve plug closing position.
-
If the model has not been selected before ordering, please provide us with the operating parameters:
(1) Nominal diameter DN (mm);
(2) Nominal pressure (MPa or bar);
(3) Fluid properties (including medium temperature, viscosity, or acidity/alkalinity);
(4) Pressure before and after the valve (pressure differential);
(5) Requirements for flow characteristics;
(6) Materials of valve body and valve core;
(7) Connection type;
(8) Driving method (provide air supply pressure, driving voltage);
(9) Supporting accessories (for pneumatic valves, it is recommended that users install an air filter triplet and a 2-position 5-way solenoid valve);
(10) On-site working conditions. -
If the product model of our company has been selected by the design unit, please order directly from our production department according to the model;
-
When the application occasion is very important or the pipeline is relatively complex, please provide the design drawings and detailed parameters as much as possible, and our experts will review and check them for you.